Hackberry
 Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis./Ulmaceae). The
genus Celtis (Hackberrys, Nettle-trees and Sugarberrys) contains
about 75 species native to North and Central America and Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis./Ulmaceae). The
genus Celtis (Hackberrys, Nettle-trees and Sugarberrys) contains
about 75 species native to North and Central America and  southern
Africa. Celtis
is the old Latin name for a species of “lotus”. The
fruits of this species were the lotus referred to in Homer’s
Odyssey. Hackberry trees can reach heights of 130 ft (40 m), with
a diameter of 4 ft (1.2 m). Hackberry has pale yellow to green
sapwood, with light brown heartwood. Hackberry wood has a straight
grain, is medium hard, bends well and has great shock resistance.
It is not stiff and is weak in compression. It works well with
most tools for most applications and is not resistant to decay.
It is used for boxes and crates, charcoal, fence posts, fuel,
furniture, millwork, plywood, sporting and athletic goods, and
veneer. The bark was used as a yellow dye southern
Africa. Celtis
is the old Latin name for a species of “lotus”. The
fruits of this species were the lotus referred to in Homer’s
Odyssey. Hackberry trees can reach heights of 130 ft (40 m), with
a diameter of 4 ft (1.2 m). Hackberry has pale yellow to green
sapwood, with light brown heartwood. Hackberry wood has a straight
grain, is medium hard, bends well and has great shock resistance.
It is not stiff and is weak in compression. It works well with
most tools for most applications and is not resistant to decay.
It is used for boxes and crates, charcoal, fence posts, fuel,
furniture, millwork, plywood, sporting and athletic goods, and
veneer. The bark was used as a yellow dye
http://www.fpl.fs.fed.us/documnts/TechSheets/HardwoodNA/pdf_files/celtismet.pdf.
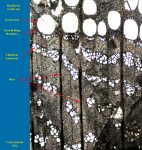
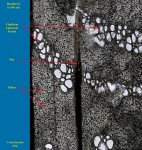
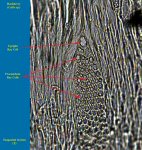
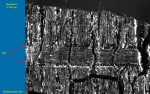
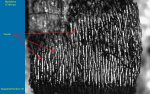
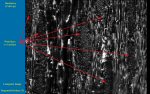
Characteristics found in the Hackberry (Celtis sp.):
- Ring porous
- Ulmiform latewood
- Spirals in vessels
- Simple perforations
- I/V pits medium (8-12)
- Rays 5-8 seriate & heterocellular
- Crystals in rays and axial parenchyma
WOOD SLIDES
Click on each image to view a larger
image.
CHARCOAL SLIDES
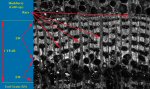  
|



 Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis./Ulmaceae). The
genus Celtis (Hackberrys, Nettle-trees and Sugarberrys) contains
about 75 species native to North and Central America and
Hackberry (Celtis occidentalis./Ulmaceae). The
genus Celtis (Hackberrys, Nettle-trees and Sugarberrys) contains
about 75 species native to North and Central America and  southern
Africa. Celtis
is the old Latin name for a species of “lotus”. The
fruits of this species were the lotus referred to in Homer’s
Odyssey. Hackberry trees can reach heights of 130 ft (40 m), with
a diameter of 4 ft (1.2 m). Hackberry has pale yellow to green
sapwood, with light brown heartwood. Hackberry wood has a straight
grain, is medium hard, bends well and has great shock resistance.
It is not stiff and is weak in compression. It works well with
most tools for most applications and is not resistant to decay.
It is used for boxes and crates, charcoal, fence posts, fuel,
furniture, millwork, plywood, sporting and athletic goods, and
veneer. The bark was used as a yellow dye
southern
Africa. Celtis
is the old Latin name for a species of “lotus”. The
fruits of this species were the lotus referred to in Homer’s
Odyssey. Hackberry trees can reach heights of 130 ft (40 m), with
a diameter of 4 ft (1.2 m). Hackberry has pale yellow to green
sapwood, with light brown heartwood. Hackberry wood has a straight
grain, is medium hard, bends well and has great shock resistance.
It is not stiff and is weak in compression. It works well with
most tools for most applications and is not resistant to decay.
It is used for boxes and crates, charcoal, fence posts, fuel,
furniture, millwork, plywood, sporting and athletic goods, and
veneer. The bark was used as a yellow dye













